ARP Protocol
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is fundamental in computer networks to map IP addresses to physical link layer addresses (MAC). Its main function is to find the MAC address associated with a specific IP address on a local network. When one device needs to communicate with another on the same network, it uses ARP to determine the MAC address of the destination before sending data.
Do you think the ARP question is a message of dissemination? Make a Wireshark capture of an ARP request and analyze it to justify your response.
Yes, it is a message of dissemination as in the header we can see that the destination has a broadcast address. This address is the one that has all its bits at 1 which in the mac addresses is translated into FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF.
When it comes to you, in this case to whom it has IP address 192.168.1.1 will return the request and in the origin we will get its MAC address.
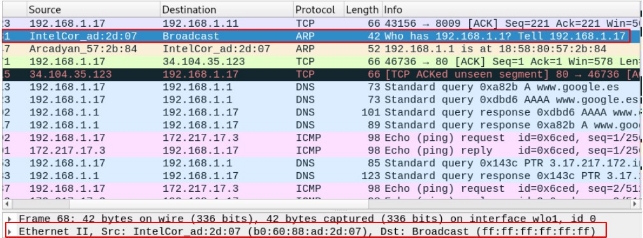
Do you think the ARP response is a message of dissemination? Make a Wireshark capture of an ARP response and analyze it to justify your response.
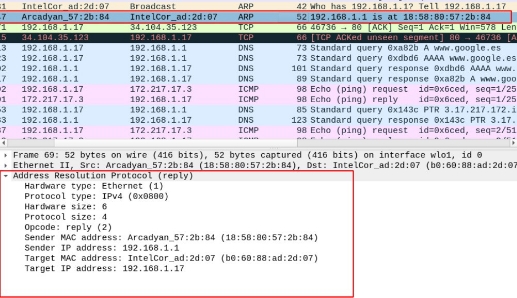
We can see in the answer that in the destination direction comes that of the pc that I send the question, so the answer is not a broadcast message but a point-by-point communication.
The computers of a network store in memory a cache with the IP-MAC correspondences they know. It explains the process of updating the ARP cache after observing how it is being filled on the machines of a small GNS3 scenario with a local network with four computers connected to a switch. See how the ARP cache of all computers changes when you go ping between one computer and another.
When we do a ping the issuer and the receiver “add each other to the ARP table”, if we consult them in both we will see that they are included:


We can see that the time they are kept in cache is 120 seconds, when this time is over, the entrance is deleted.
While in the pcs that have not intervened they will not store anything in the cache arp on the “transaction made”:


Analyze the ip neigh command to see the possibilities it offers and think about what the real use of each of them can be.
This command allows us to interact with the arp table where the IP-MAC address ratio is saved. For example, we can view it, add inputs or delete them and modify them. We can also change the time during which a request is saved in the table.
For example, list the content:

We can summarize your functions:
- Show the full ARP table: ip neighbourhood show
- Add an entry to the ARP table: ip near add (IP) laddr {MAC} dev {interface}
- Remove an entry from the ARP table: ip nearby from the {IP} dev {interface}
- Set the life time of an entry in the ARP table: ip neighbourhood change {IP} dev {interface} nud {state}
- Search for a specific entry in the ARP table: ip near 124; grep {IP}
Basically this is what we need to know to be able to control the ARP tables with the IP command in replacement (or as a complement) to “arp.”
Find out what a free ARP is and what the meaning of its existence is.
It is a request issued by a device in order to update the arp table of the other devices of a network. It simply informs other network devices of its own IP and MAC address.
The main purpose of free ARP is to ensure that all devices on a network have the most up-to-date information possible on the IP and MAC addresses of other devices on the network.
One of its utilities is to detect IP’s conflicts, “this ip is already taken” this is because another team has responded with these packages.
Therefore, from this information this incidence can be resolved.
Explain with your words what an ARP Spofing attack is based on and how it is carried out. Can it be used as an attack technique from your home to an alien network? How could we defend ourselves against him?
The attack changes the flow of data sent from a Victim PC that passes through a Gateway to make a MITM (Man in the Middle) attack by getting the victim’s traffic through an Attack machine in a manner that is safe for the victim.
Thus the attacker intercepts the messages and is able to obtain all the traffic from the network by obtaining passwords and confidential or sensitive information.
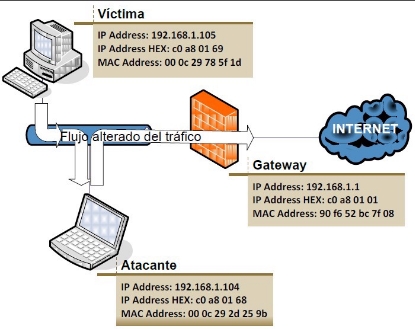
The steps followed by an attacker in carrying out this attack are:
- Scanning the network, to get a relationship of the connected devices.
- Send false arp packages to associate your ip address to your own mac.
- Once the client has been “deceived,” the attacker will start intercepting all the traffic.
These attacks only occur if the attacker gets access to your local network, so to protect ourselves we can use:
- ARP Spofing detection tools.
- Use a firewall as it is able to block suspicious ARP packages.
- Use protocols like Ipsec and SSL / TLS.
- Configure the arp table in a static way.
There are two types of switch attacks called MAC Flooding and MAC Spofing. What are they and how can we defend ourselves from them?
MAC Flooding consists of filling the arp table of a network device, for example a switch and making it not able to locate to which mouth the traffic goes to if it sends it through all the mouths causing at worst to leave the device out of service.
To mitigate this attack it is recommended to set a limit on the size of the ARP table and the detection and blocking of suspicious traffic.
While the MAC Spofing consists of falsifying a MAC address to intercept a particular traffic, it can have access to private content.
To mitigate this attack in the event that you supply a machine from my network and have access to content we can implement second factor authentication tools or use digital certificates.
We can also implement the following strategies in our network:
Static inputs to ARP table
The first solution that exists is to work with static routes in network equipment. This allows to invalidate ARP messages, because the IP is associated with a MAC address and this does not change over time. It is a simple and generally applied solution to ensure that the predetermined link door is really that of the network and not an attacker. However, it is a difficult strategy to apply if you have a network with a lot of terminals.
DHCP snooping
It is a strategy that keeps a record of the MAC that are connected in each port and immediately detects if there is a subplanting. Several network equipment manufacturers incorporate this solution into their equipment, such as CISCO.
Dynamic ARP Inspection
To prevent the supplanting of ARP (ARP spoofing) and the resulting ARP poisoning (ARP poisoning), a switch should ensure that only ARP Requests and ARP Replies are transmitted valid.
The Dynamic ARP / Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) Dynamic Inspection requires DHCP snooping and helps prevent ARP attacks as follows:
- Not transmitting invalid or free / free ARP responses / Replies to other ports in the same VLAN.
- Intercept all requests / Requests and answers / Replies ARP in unreliable ports.
- Checking each intercepted package for a valid IP to MAC link.
- Discard and record invalid ARP responses to prevent ARP poisoning.
- Error-disabling the interface if you exceed the number of ARP DAI packages configured.
RARP
RARP is Reversal ARP, which means that you consult the corresponding IP from a MAC address. In case you return more than one IP address, then the MAC has been cloned.
